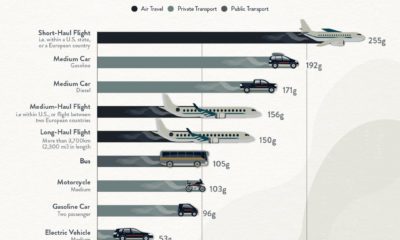
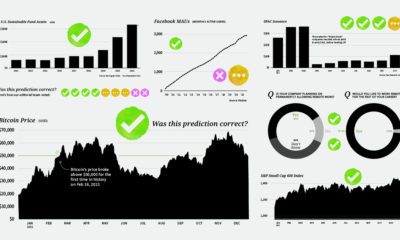
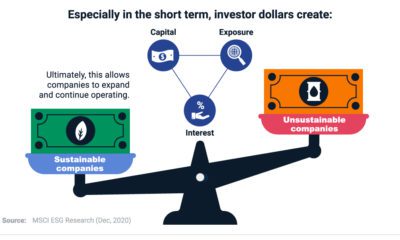
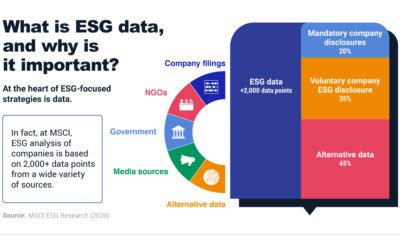
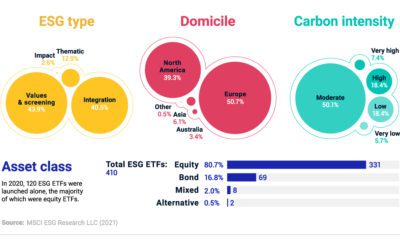
Against all odds, sustainable investing in the U.S. smashed records in 2020. Estimated net flows reached $20.9 billion in the first six months alone—that’s nearly equal to the amount of new money invested in all of 2019. What is driving the shift to sustainable investing? This visual dashboard from Raconteur explains five key drivers, from generational shifts to investors’ preferred strategies.
Millennial Investors and Personal Beliefs
Interest in sustainable investing is booming across the general population. However, there’s a clear generational trend, as well. While the portion of each group that is “very interested” in sustainable investing has shot up since 2015, this share is significantly higher for millennials. Another correlated trend emerges with this. These days, investors are more likely to follow their conscience. Acccording to a recent report by Schroders, the majority of investors will not budge on investing against their beliefs, even if returns were theoretically higher.
Top Themes of Interest
Powered by these personal beliefs, which categories are attracting investors? It turns out many investors are very interested in including environment-related themes into their portfolios:
Plastic reduction: 46% Climate change: 46% Community development: 42% Circular economy: 39% Sustainable Development Goals: 36% Multicultural diversity: 30% Gender diversity: 30% Faith-based values: 24%
However, these aren’t the only considerations. Other themes that fit into broader ESG categories such as gender diversity or faith-based values make an appearance, too.
Which Investor Groups are Driving Interest?
Now, we turn our attention to the specific groups that are responsible for the growing momentum towards sustainable investing. This may be surprising to some, but it is institutional investors that are leading the pack by far: This also disproves a common myth that millennials are the only ones interested in the sector. Institutional investors equally want to see a double bottom line: an ROI on their money, while also making the world a more sustainable place.
Sources of Information
So where are institutional investors sourcing their information around sustainable investing? Sharing their ideas in like-minded communities, such as webinars and conferences emerged as the preference for nearly two-thirds of those surveyed in this group. But how do investors know that their investment is truly sustainable? For this, 34% of global investors feel that third-party labels from independent organizations help lend credibility, and confirm that the chosen investment in question is indeed carried out in a responsible manner. As more and more institutional investors are digital natives, a significant share of them are also beginning to use social media to influence their decision-making process—and some even rely on it as their key source of research.
Sustainable Investing Strategies
We’ve left the best for last—armed with this knowledge and confidence, which sustainable investing strategies are the most attractive? Here’s how organizations are approaching ESG:
Sustainability integration: 52% Negative screening: 50% Shareholder engagement: 31% Impact investing: 19% Positive screening: 12% Thematic investing: 5%
While negative screening—avoiding investments in “sin” stocks such as tobacco or fossil fuels—is still a popular strategy, actively integrating sustainability into one’s portfolio is emerging more front and center.
The Overall Trend of Sustainable Investing
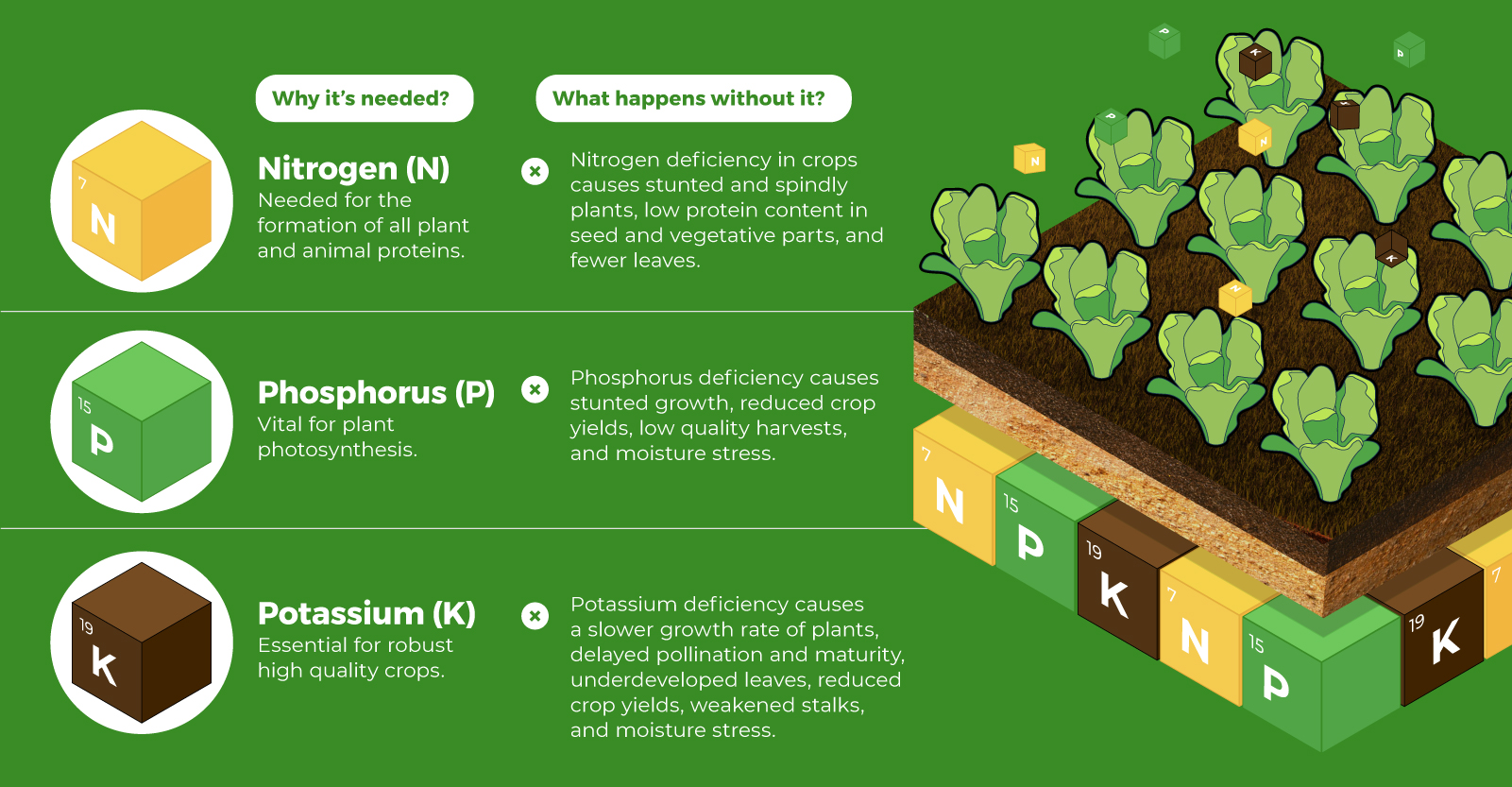
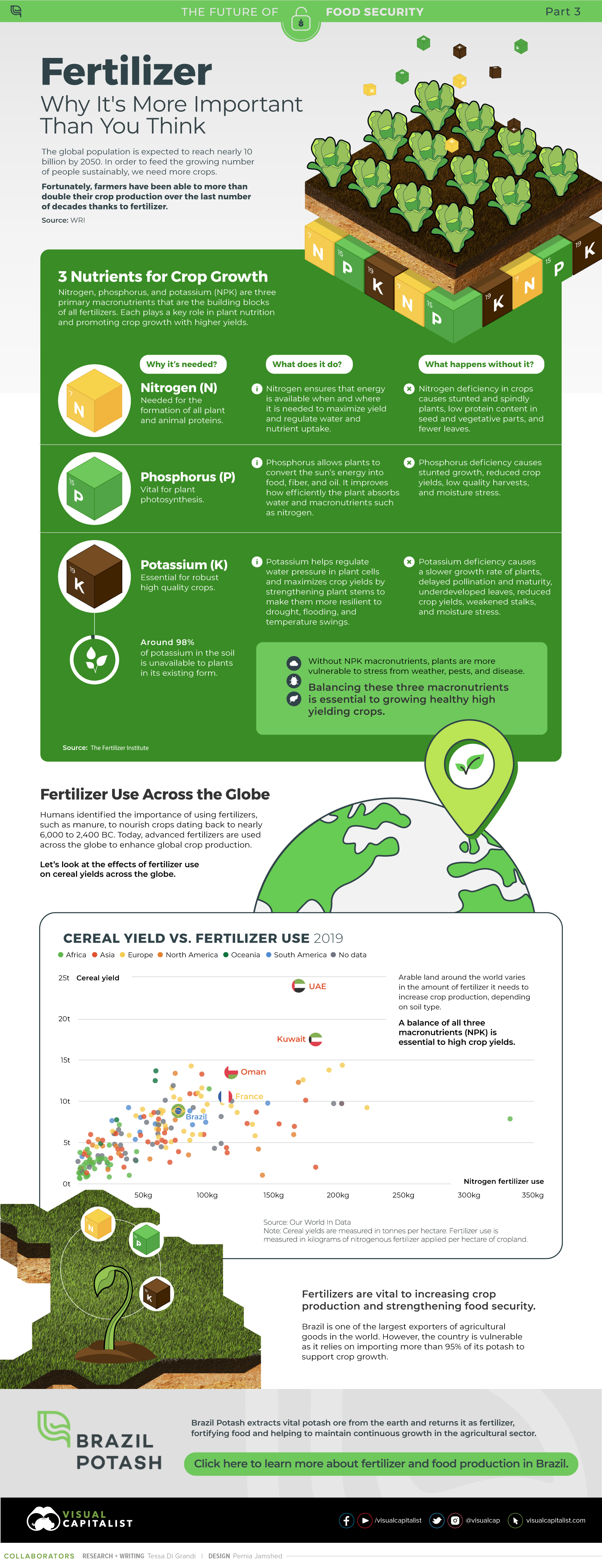
The data makes clear that institutional investors are the main driving forces behind sustainable investment for the time being. But as millennials accumulate wealth, their values may naturally lead them towards more sustainable investment. Another important point to note is that sustainable investing has been resilient to change. In fact, despite the COVID-induced stock selloff in early 2020, ESG leaders exceeded expectations. While these drivers evolve over time, it’s clear that sustainable investing is more than having its moment in the spotlight—it’s here to stay. on Over recent decades, farmers have been able to more than double their production of crops thanks to fertilizers and the vital nutrients they contain. When crops are harvested, the essential nutrients are taken away with them to the dining table, resulting in the depletion of these nutrients in the soil. To replenish these nutrients, fertilizers are needed, and the cycle continues. The above infographic by Brazil Potash shows the role that each macronutrient plays in growing healthy, high-yielding crops.
Food for Growth
Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium (NPK) are three primary macronutrients that are the building blocks of the global fertilizer industry. Each plays a key role in plant nutrition and promoting crop growth with higher yields. Let’s take a look at how each macronutrient affects plant growth. If crops lack NPK macronutrients, they become vulnerable to various stresses caused by weather conditions, pests, and diseases. Therefore, it is crucial to maintain a balance of all three macronutrients for the production of healthy, high-yielding crops.
The Importance of Fertilizers
Humans identified the importance of using fertilizers, such as manure, to nourish crops dating back to nearly 6,000 to 2,400 BC. As agriculture became more intensive and large-scale, farmers began to experiment with different types of fertilizers. Today advanced chemical fertilizers are used across the globe to enhance global crop production. There are a myriad of factors that affect soil type, and so the farmable land must have a healthy balance of all three macronutrients to support high-yielding, healthy crops. Consequently, arable land around the world varies in the amount and type of fertilizer it needs. Fertilizers play an integral role in strengthening food security, and a supply of locally available fertilizer is needed in supporting global food systems in an ever-growing world. Brazil is one of the largest exporters of agricultural goods in the world. However, the country is vulnerable as it relies on importing more than 95% of its potash to support crop growth. Brazil Potash is developing a new potash project in Brazil to ensure a stable domestic source of this nutrient-rich fertilizer critical for global food security. Click here to learn more about fertilizer and food production in Brazil.