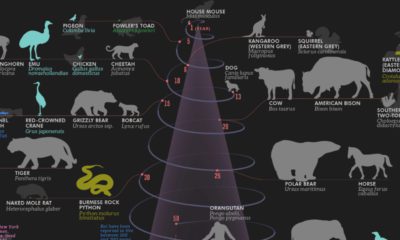
The World’s Most Famous Diamonds
The stories and histories of the most famous diamonds
You may have heard of the Cullinan Diamond or the Hope Diamond before, but do you know the stories behind these legendary finds?
Today’s infographic looks at the history and characteristics of six of the most famous diamonds.
A Diamond Primer
Every diamond is unique, and as a result the value of a particular diamond is partially determined by the eye of the beholder. The diamond industry generally uses a set of criteria called the Four C’s to help evaluate the potential value of a diamond: Clarity, Cut, Carats, and Color.
Most diamonds found have major deficiencies in one or more of the above categories. For example, while a diamond may be clear and large in size, it may have a less desirable color and shape. In a previous infographic, we explain the importance of these characteristics in more depth, and we’ve also previously posted on the significance of rare-colored diamonds.
The most famous diamonds in the world are exceptionally rare: they tend to excel in all four of the above categories. They are a desired color and shape, have great clarity, and are giant in size.
The Most Famous Diamonds
The stories behind six of the most famous diamonds in brief:
The Cullinan Diamond: Perhaps the most well-known, the Cullinan Diamond was discovered in 1905 in South Africa. Weighing in at 3,106.75 carats, the Cullinan is the largest rough gem-quality diamond ever discovered. The diamond was ultimately cut into nine smaller stones including the 530.20 carat Star of Africa, which is valued at over $400 million alone.
The Hope Diamond: The Hope Diamond is a grayish-blue diamond that was discovered in India at an unknown date. It has a long history, in which it changed hands numerous times between countries and eventually ended up at the Smithsonian Institute in Washington, D.C.
The Centenary Diamond: The Centenary Diamond is considered to be one of the most flawless diamonds, both internally and externally. Discovered in South Africa, it was unveiled in its final form by De Beers in 1991. The current owner is unknown.
The Regent Diamond: This pale blue diamond was discovered by a slave in India in 1698. After eventually making it to the crowns of Louis XV and Louis XVI in France, it is now on display at the Louvre in Paris and weighs 140.64 carats.
The Koh-i-Noor Diamond: Meaning “Mountain of Light” in the Persian language, this diamond was discovered at a mine in India. It is of the finest white color, and made its way from a Hindu temple eventually to the Crown of Queen Elizabeth in 1850.
The Orlov Diamond: Discovered in India at an unknown date, this jewel retains its traditional Indian rose-style cut. The Orlov, which weighs in at 189.62 carats and is white with a faint bluish-green color, now rests in the Kremlin in Russia.
The world’s most famous diamonds all have intriguing stories behind their discoveries. However, a diamond prospector doesn’t need to find a diamond to strike it rich: check out the infographic story of Diamond Fields, a diamond company that ended up finding and auctioning off one of the world’s richest nickel deposits for billions.
Original graphic by: Gear Jewellers
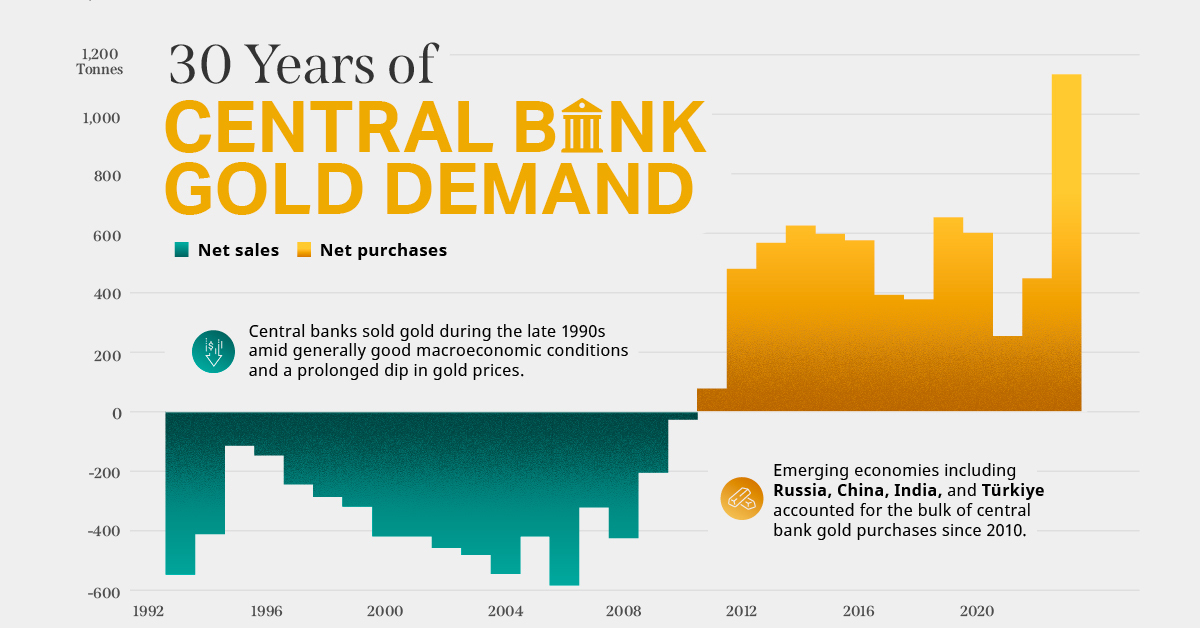
on Did you know that nearly one-fifth of all the gold ever mined is held by central banks? Besides investors and jewelry consumers, central banks are a major source of gold demand. In fact, in 2022, central banks snapped up gold at the fastest pace since 1967. However, the record gold purchases of 2022 are in stark contrast to the 1990s and early 2000s, when central banks were net sellers of gold. The above infographic uses data from the World Gold Council to show 30 years of central bank gold demand, highlighting how official attitudes toward gold have changed in the last 30 years.
Why Do Central Banks Buy Gold?
Gold plays an important role in the financial reserves of numerous nations. Here are three of the reasons why central banks hold gold:
Balancing foreign exchange reserves Central banks have long held gold as part of their reserves to manage risk from currency holdings and to promote stability during economic turmoil. Hedging against fiat currencies Gold offers a hedge against the eroding purchasing power of currencies (mainly the U.S. dollar) due to inflation. Diversifying portfolios Gold has an inverse correlation with the U.S. dollar. When the dollar falls in value, gold prices tend to rise, protecting central banks from volatility. The Switch from Selling to Buying In the 1990s and early 2000s, central banks were net sellers of gold. There were several reasons behind the selling, including good macroeconomic conditions and a downward trend in gold prices. Due to strong economic growth, gold’s safe-haven properties were less valuable, and low returns made it unattractive as an investment. Central bank attitudes toward gold started changing following the 1997 Asian financial crisis and then later, the 2007–08 financial crisis. Since 2010, central banks have been net buyers of gold on an annual basis. Here’s a look at the 10 largest official buyers of gold from the end of 1999 to end of 2021: Rank CountryAmount of Gold Bought (tonnes)% of All Buying #1🇷🇺 Russia 1,88828% #2🇨🇳 China 1,55223% #3🇹🇷 Türkiye 5418% #4🇮🇳 India 3956% #5🇰🇿 Kazakhstan 3455% #6🇺🇿 Uzbekistan 3115% #7🇸🇦 Saudi Arabia 1803% #8🇹🇭 Thailand 1682% #9🇵🇱 Poland1282% #10🇲🇽 Mexico 1152% Total5,62384% Source: IMF The top 10 official buyers of gold between end-1999 and end-2021 represent 84% of all the gold bought by central banks during this period. Russia and China—arguably the United States’ top geopolitical rivals—have been the largest gold buyers over the last two decades. Russia, in particular, accelerated its gold purchases after being hit by Western sanctions following its annexation of Crimea in 2014. Interestingly, the majority of nations on the above list are emerging economies. These countries have likely been stockpiling gold to hedge against financial and geopolitical risks affecting currencies, primarily the U.S. dollar. Meanwhile, European nations including Switzerland, France, Netherlands, and the UK were the largest sellers of gold between 1999 and 2021, under the Central Bank Gold Agreement (CBGA) framework. Which Central Banks Bought Gold in 2022? In 2022, central banks bought a record 1,136 tonnes of gold, worth around $70 billion. Country2022 Gold Purchases (tonnes)% of Total 🇹🇷 Türkiye14813% 🇨🇳 China 625% 🇪🇬 Egypt 474% 🇶🇦 Qatar333% 🇮🇶 Iraq 343% 🇮🇳 India 333% 🇦🇪 UAE 252% 🇰🇬 Kyrgyzstan 61% 🇹🇯 Tajikistan 40.4% 🇪🇨 Ecuador 30.3% 🌍 Unreported 74165% Total1,136100% Türkiye, experiencing 86% year-over-year inflation as of October 2022, was the largest buyer, adding 148 tonnes to its reserves. China continued its gold-buying spree with 62 tonnes added in the months of November and December, amid rising geopolitical tensions with the United States. Overall, emerging markets continued the trend that started in the 2000s, accounting for the bulk of gold purchases. Meanwhile, a significant two-thirds, or 741 tonnes of official gold purchases were unreported in 2022. According to analysts, unreported gold purchases are likely to have come from countries like China and Russia, who are looking to de-dollarize global trade to circumvent Western sanctions.
There were several reasons behind the selling, including good macroeconomic conditions and a downward trend in gold prices. Due to strong economic growth, gold’s safe-haven properties were less valuable, and low returns made it unattractive as an investment.
Central bank attitudes toward gold started changing following the 1997 Asian financial crisis and then later, the 2007–08 financial crisis. Since 2010, central banks have been net buyers of gold on an annual basis.
Here’s a look at the 10 largest official buyers of gold from the end of 1999 to end of 2021:
Source: IMF
The top 10 official buyers of gold between end-1999 and end-2021 represent 84% of all the gold bought by central banks during this period.
Russia and China—arguably the United States’ top geopolitical rivals—have been the largest gold buyers over the last two decades. Russia, in particular, accelerated its gold purchases after being hit by Western sanctions following its annexation of Crimea in 2014.
Interestingly, the majority of nations on the above list are emerging economies. These countries have likely been stockpiling gold to hedge against financial and geopolitical risks affecting currencies, primarily the U.S. dollar.
Meanwhile, European nations including Switzerland, France, Netherlands, and the UK were the largest sellers of gold between 1999 and 2021, under the Central Bank Gold Agreement (CBGA) framework.
Which Central Banks Bought Gold in 2022?
In 2022, central banks bought a record 1,136 tonnes of gold, worth around $70 billion. Türkiye, experiencing 86% year-over-year inflation as of October 2022, was the largest buyer, adding 148 tonnes to its reserves. China continued its gold-buying spree with 62 tonnes added in the months of November and December, amid rising geopolitical tensions with the United States. Overall, emerging markets continued the trend that started in the 2000s, accounting for the bulk of gold purchases. Meanwhile, a significant two-thirds, or 741 tonnes of official gold purchases were unreported in 2022. According to analysts, unreported gold purchases are likely to have come from countries like China and Russia, who are looking to de-dollarize global trade to circumvent Western sanctions.