On the one hand, there are many people struggling to make ends meet, and a higher minimum wage could certainly impact the 10 million working poor spread throughout the country. Not only would it help some of these workers sustain better living standards, but some research also shows that an increase can actually help certain types of businesses, and that job losses from a higher wage are usually minimal. From another angle, however, many economists see a higher minimum wage as any other supply and demand situation. Arbitrarily raising the price of labor limits the demand for that labor – and in places like Seattle, recent studies have shown that the minimum wage increase is hurting the people it is supposed to help. To complicate things even further, the prospect of increased automation in the workplace is also a factor that affects these outcomes.
The Real Minimum Wage in Context
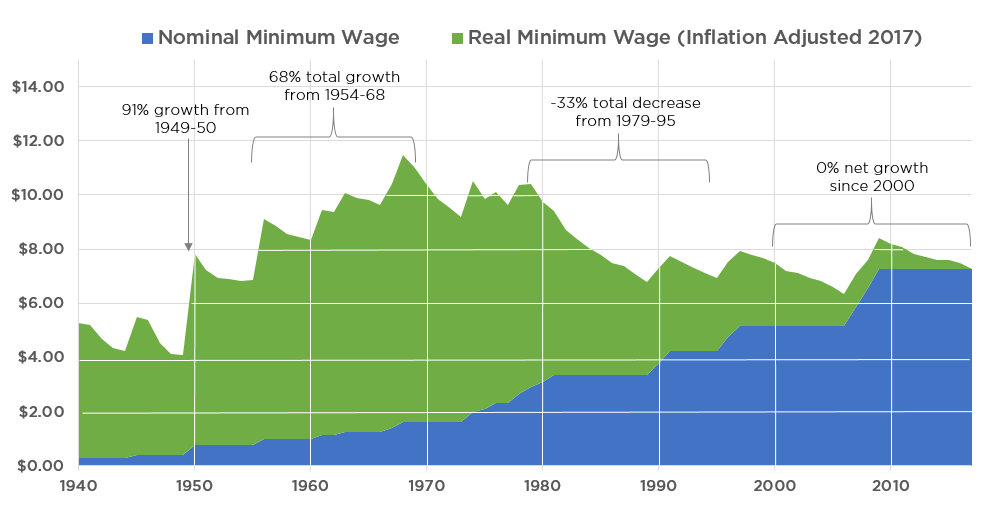
Putting this debate aside, today’s visualization from cost information site HowMuch.net reveals some interesting points to consider about the minimum wage, which help put the numbers in context. By adjusting the minimum wage for the Consumer Price Index (CPI) over time, it shows that in the last 25 years there has been no real increase in the minimum wage. Inflation has quickly erased any adjustments, keeping it stagnant for years. Further, in real terms, the minimum wage peaked in value in 1968, just before Nixon severed the connection between the dollar and gold. In the inflationary years that followed, the real minimum wage eventually dropped to $6.77, a staggering 41.0% decrease. The real wage has basically hovered between $6.50 and $8.00 ever since.
Precious metals advocates make an important point about this: the minimum wage in nominal terms in 1964 was $1.25, or five silver quarters. If you were to cash in that silver today (~$17.15 per oz), the melt value would be $15.50, which is actually double the current minimum wage.
Action at State and City Levels
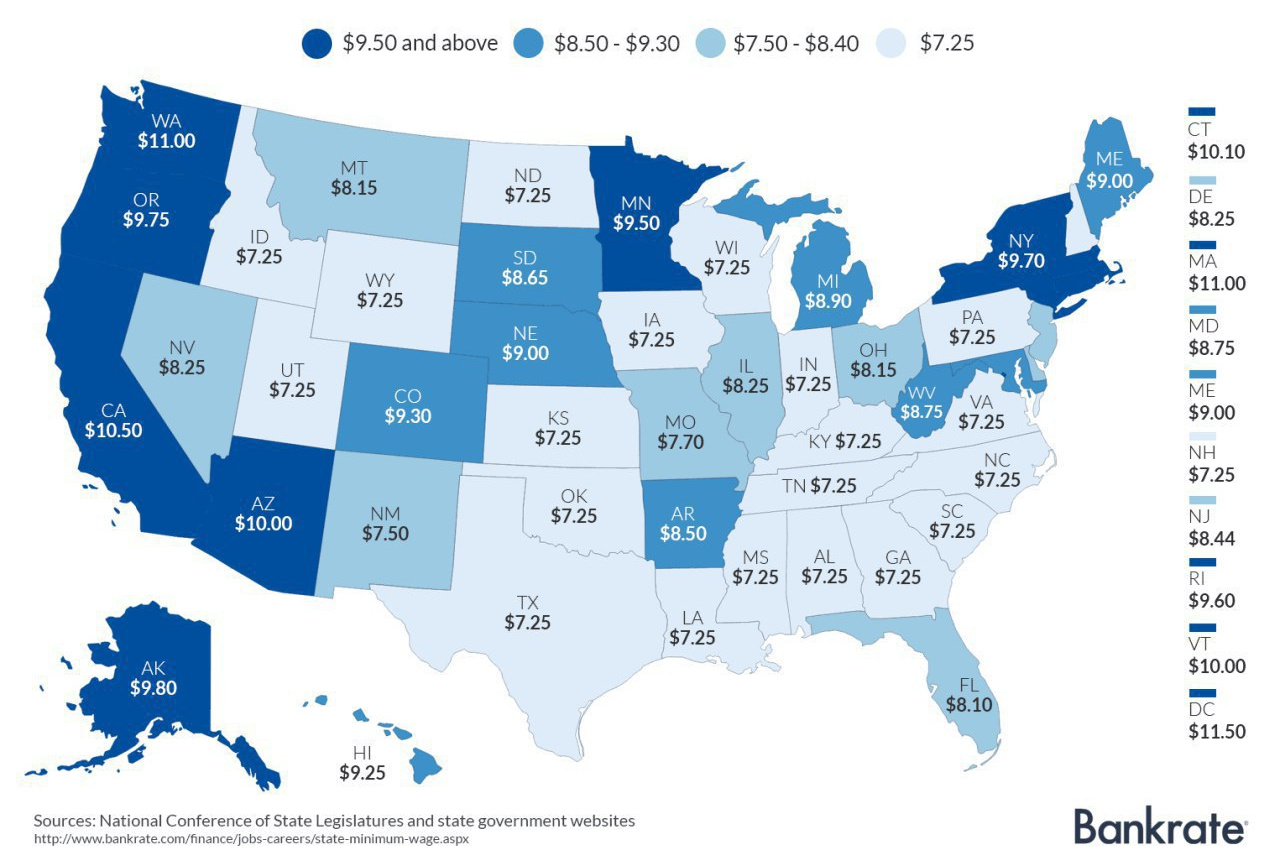
Today, the majority of U.S. states have higher minimum wages than the federal amount of $7.25. States with the highest minimum wages include Washington ($11.00), Massachusetts ($11.00), California ($10.50), Vermont ($10.00), Arizona ($10.00), and Connecticut ($10.00). Washington, D.C. also has its minimum set at $11.50. Here are the 29 states that have higher minimums, according to Bankrate.com:
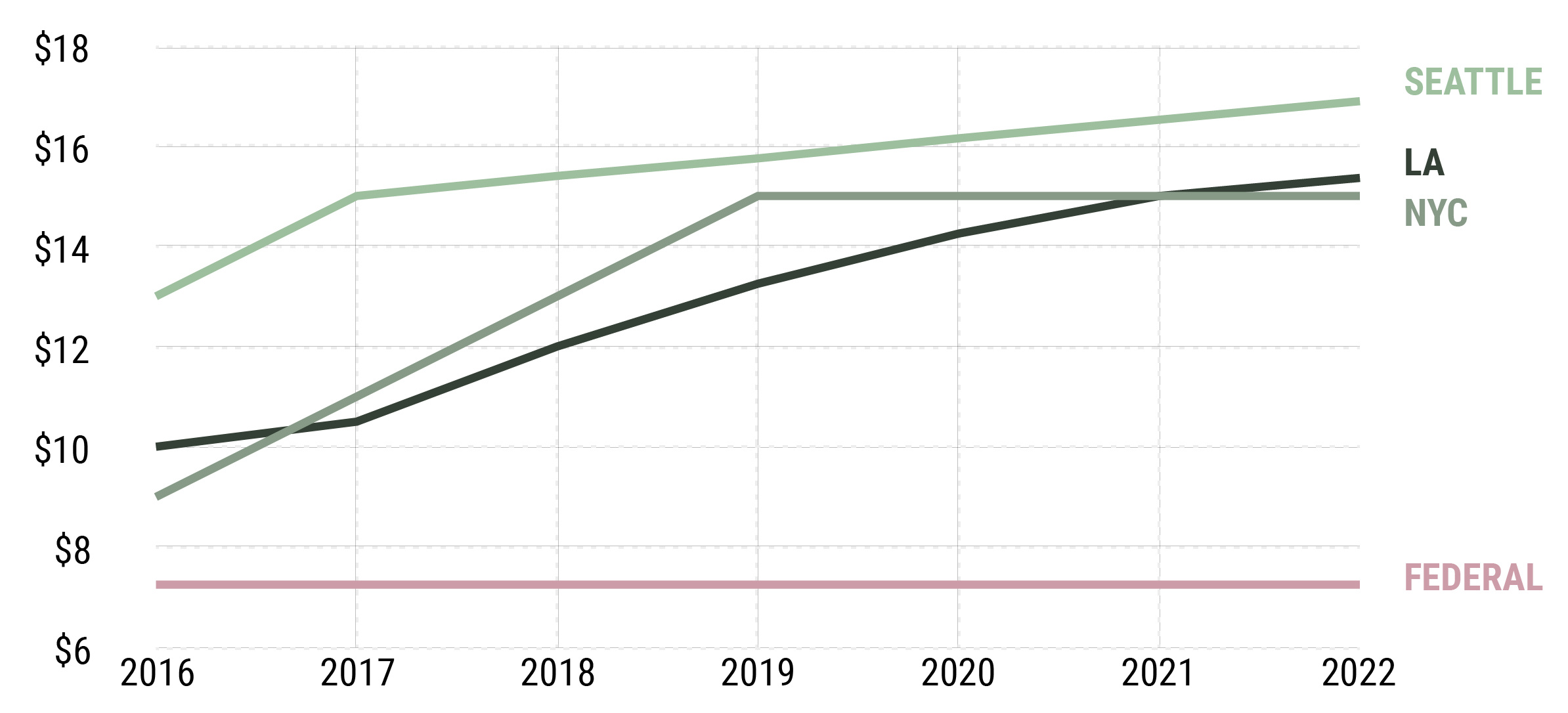
And here are the upcoming schedules for the minimum wage increases in some major cities, including Los Angeles, Seattle, and New York City.
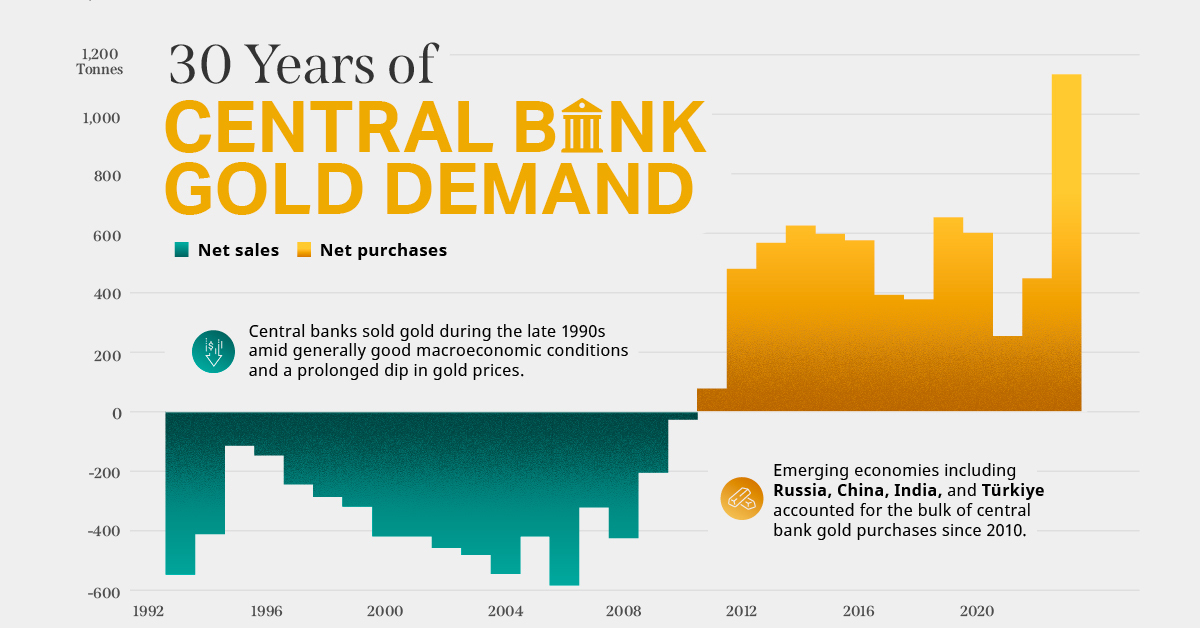
By 2025, the highly-debated Seattle minimum wage is anticipated to hit $18.00 for all types of businesses. on Did you know that nearly one-fifth of all the gold ever mined is held by central banks? Besides investors and jewelry consumers, central banks are a major source of gold demand. In fact, in 2022, central banks snapped up gold at the fastest pace since 1967. However, the record gold purchases of 2022 are in stark contrast to the 1990s and early 2000s, when central banks were net sellers of gold. The above infographic uses data from the World Gold Council to show 30 years of central bank gold demand, highlighting how official attitudes toward gold have changed in the last 30 years.
Why Do Central Banks Buy Gold?
Gold plays an important role in the financial reserves of numerous nations. Here are three of the reasons why central banks hold gold:
Balancing foreign exchange reserves Central banks have long held gold as part of their reserves to manage risk from currency holdings and to promote stability during economic turmoil. Hedging against fiat currencies Gold offers a hedge against the eroding purchasing power of currencies (mainly the U.S. dollar) due to inflation. Diversifying portfolios Gold has an inverse correlation with the U.S. dollar. When the dollar falls in value, gold prices tend to rise, protecting central banks from volatility. The Switch from Selling to Buying In the 1990s and early 2000s, central banks were net sellers of gold. There were several reasons behind the selling, including good macroeconomic conditions and a downward trend in gold prices. Due to strong economic growth, gold’s safe-haven properties were less valuable, and low returns made it unattractive as an investment. Central bank attitudes toward gold started changing following the 1997 Asian financial crisis and then later, the 2007–08 financial crisis. Since 2010, central banks have been net buyers of gold on an annual basis. Here’s a look at the 10 largest official buyers of gold from the end of 1999 to end of 2021: Rank CountryAmount of Gold Bought (tonnes)% of All Buying #1🇷🇺 Russia 1,88828% #2🇨🇳 China 1,55223% #3🇹🇷 Türkiye 5418% #4🇮🇳 India 3956% #5🇰🇿 Kazakhstan 3455% #6🇺🇿 Uzbekistan 3115% #7🇸🇦 Saudi Arabia 1803% #8🇹🇭 Thailand 1682% #9🇵🇱 Poland1282% #10🇲🇽 Mexico 1152% Total5,62384% Source: IMF The top 10 official buyers of gold between end-1999 and end-2021 represent 84% of all the gold bought by central banks during this period. Russia and China—arguably the United States’ top geopolitical rivals—have been the largest gold buyers over the last two decades. Russia, in particular, accelerated its gold purchases after being hit by Western sanctions following its annexation of Crimea in 2014. Interestingly, the majority of nations on the above list are emerging economies. These countries have likely been stockpiling gold to hedge against financial and geopolitical risks affecting currencies, primarily the U.S. dollar. Meanwhile, European nations including Switzerland, France, Netherlands, and the UK were the largest sellers of gold between 1999 and 2021, under the Central Bank Gold Agreement (CBGA) framework. Which Central Banks Bought Gold in 2022? In 2022, central banks bought a record 1,136 tonnes of gold, worth around $70 billion. Country2022 Gold Purchases (tonnes)% of Total 🇹🇷 Türkiye14813% 🇨🇳 China 625% 🇪🇬 Egypt 474% 🇶🇦 Qatar333% 🇮🇶 Iraq 343% 🇮🇳 India 333% 🇦🇪 UAE 252% 🇰🇬 Kyrgyzstan 61% 🇹🇯 Tajikistan 40.4% 🇪🇨 Ecuador 30.3% 🌍 Unreported 74165% Total1,136100% Türkiye, experiencing 86% year-over-year inflation as of October 2022, was the largest buyer, adding 148 tonnes to its reserves. China continued its gold-buying spree with 62 tonnes added in the months of November and December, amid rising geopolitical tensions with the United States. Overall, emerging markets continued the trend that started in the 2000s, accounting for the bulk of gold purchases. Meanwhile, a significant two-thirds, or 741 tonnes of official gold purchases were unreported in 2022. According to analysts, unreported gold purchases are likely to have come from countries like China and Russia, who are looking to de-dollarize global trade to circumvent Western sanctions.
There were several reasons behind the selling, including good macroeconomic conditions and a downward trend in gold prices. Due to strong economic growth, gold’s safe-haven properties were less valuable, and low returns made it unattractive as an investment.
Central bank attitudes toward gold started changing following the 1997 Asian financial crisis and then later, the 2007–08 financial crisis. Since 2010, central banks have been net buyers of gold on an annual basis.
Here’s a look at the 10 largest official buyers of gold from the end of 1999 to end of 2021:
Source: IMF
The top 10 official buyers of gold between end-1999 and end-2021 represent 84% of all the gold bought by central banks during this period.
Russia and China—arguably the United States’ top geopolitical rivals—have been the largest gold buyers over the last two decades. Russia, in particular, accelerated its gold purchases after being hit by Western sanctions following its annexation of Crimea in 2014.
Interestingly, the majority of nations on the above list are emerging economies. These countries have likely been stockpiling gold to hedge against financial and geopolitical risks affecting currencies, primarily the U.S. dollar.
Meanwhile, European nations including Switzerland, France, Netherlands, and the UK were the largest sellers of gold between 1999 and 2021, under the Central Bank Gold Agreement (CBGA) framework.
Which Central Banks Bought Gold in 2022?
In 2022, central banks bought a record 1,136 tonnes of gold, worth around $70 billion. Türkiye, experiencing 86% year-over-year inflation as of October 2022, was the largest buyer, adding 148 tonnes to its reserves. China continued its gold-buying spree with 62 tonnes added in the months of November and December, amid rising geopolitical tensions with the United States. Overall, emerging markets continued the trend that started in the 2000s, accounting for the bulk of gold purchases. Meanwhile, a significant two-thirds, or 741 tonnes of official gold purchases were unreported in 2022. According to analysts, unreported gold purchases are likely to have come from countries like China and Russia, who are looking to de-dollarize global trade to circumvent Western sanctions.